What is photobiomodulation?
This therapy aims to support the body’s natural healing process and address various health issues.
Photobiomodulation (short: PBM)
Photobiomodulation (PBM), also known as red light therapy (RLT), is a method for promoting the healing and regeneration of tissue through the use of light waves in the red and near-infrared spectrum. Its roots are in classical red light therapy, which originally used incandescent lamps with red light filters. However, due to the heat produced, this method had limitations in light intensity and did not allow for precise control over the light spectrum.
This therapy aims to support the body’s natural healing process and address various health issues.
Technological Development: From the Red Light Lamp to Photobiomodulation
Modern advancements in LED technology have evolved traditional red light therapy into a more effective form of photobiomodulation. This involves the targeted use of light waves in the red and near-infrared spectrum (specifically 660 nm and 850 nm) to optimally stimulate cells and mitochondria. Today’s technology allows for more intense light exposure with minimal heat generation, leading to the term “cold red light.”
Origins of Photobiomodulation
The first scientific insights into the effects of PBM date back to 1967. The Hungarian doctor Endre Mester discovered in an experiment with laser light that instead of negative effects, hair growth in mice was accelerated. This discovery led to the development of what is known as “Low-Level Laser Therapy” (LLLT), which later became known as Photobiomodulation. The positive effect was attributed to the specific light spectrum of the laser (660 nm). Thanks to LED technology, other light wavelengths such as near-infrared light (850 nm) can now be used efficiently.
Mechanism of Photobiomodulation
In photobiomodulation, low-intensity light, typically in the range of 600 to 1000 nanometers (nm), is applied to the skin. This light penetrates the skin layers and is absorbed by the cells, particularly by the mitochondria (the energy powerhouses of cells). A central mechanism of PBM lies in influencing the mitochondrial respiratory chain. The red and near-infrared light waves stimulate an enzyme in the mitochondria, cytochrome c oxidase, which captures the energy of photons and optimizes ATP production. This leads to accelerated cell regeneration and energy production.
The main mechanisms of photobiomodulation include
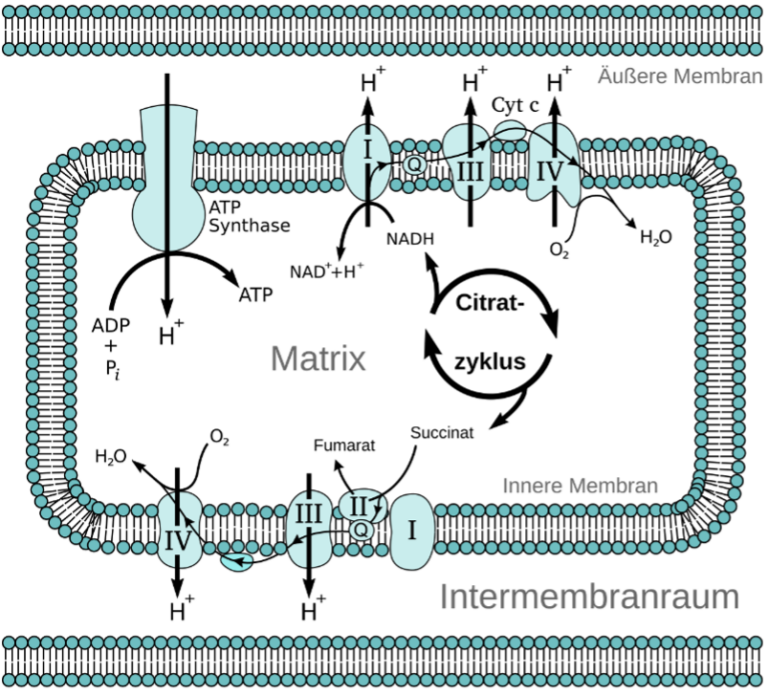
Picture source: https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmungskette
Stimulation of cell energy production
The light activates the mitochondria in the cells, which increases the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the primary energy source of the cells, and an increased energy production promotes cell regeneration and repair.
Promotion of cell regeneration and repair
By improving cellular energy and increasing ATP production, the regeneration of damaged tissues is supported. This is particularly useful in the healing of wounds, injuries, and inflammation.
Reduction of Inflammation
Photobiomodulation has anti-inflammatory effects by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory molecules and increasing the activity of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Pain relief
Through improving blood circulation and reducing inflammation, photobiomodulation can alleviate pain by addressing its underlying causes.
Promotion of Skin Health
The therapy can improve skin elasticity, stimulate collagen production, and refine the complexion, leading to a younger and healthier appearance.
Benefits of Photobiomodulation
Photobiomodulation offers a variety of benefits for patients and practitioners seeking effective and non-invasive treatment methods. The key advantages include:
Accelerated healing of wounds and injuries
Through the stimulation of cell regeneration and the enhancement of energy production, photobiomodulation promotes the rapid healing of wounds and injuries.
Improved Skin Health
The stimulation of collagen production and the improvement of skin elasticity contribute to a healthier and more youthful appearance. This can also be helpful in treating skin disorders and signs of aging.
Pain relief and reduction of inflammation
The therapy offers an effective method for alleviating chronic pain and reducing inflammation, leading to an improved quality of life.
Support in Recovery After Injuries
The therapy can accelerate rehabilitation after injuries by supporting tissue regeneration and optimizing the healing processes.
Application in Prevention
In addition to treating existing ailments, photobiomodulation can also be used for health prevention. It supports overall well-being and can help maintain health in the long term.
Comparison to Infrared Therapy
While traditional infrared therapy works through heat and can be helpful for colds, muscle tension, and joint diseases, PBM focuses on the cellular and molecular level to optimize health and treat a wide range of conditions. Both methods have their specific advantages and applications.
Conclusion
Photobiomodulation is an advanced therapy that offers numerous health benefits through the application of light energy. It promotes cell regeneration, reduces inflammation and pain, enhances skin health, and supports the healing of wounds and injuries. Patients benefit from a gentle, non-invasive method that supports the body’s natural healing ability and enhances overall well-being.